Highfield International
Level 4 Award in Food Safety Management for Manufacturing
The Highfield Level 4 Award equips managers, supervisors, and aspiring leaders with the advanced knowledge to design, implement, and audit robust food safety management systems within a manufacturing environment.

Course Overview
The Highfield Level 4 Award in Food Safety Management for Manufacturing is an advanced qualification designed for professionals responsible for developing, managing, and verifying food safety systems within food manufacturing and processing environments.
This course goes beyond basic food hygiene, focusing on risk-based management, legal compliance, HACCP principles, and continuous improvement in complex manufacturing environments.
It is ideal for those who play a strategic role in food safety decision-making and compliance.
Why Choose the Level 4 Award in Food Safety Management for Manufacturing?

HACCP Mastery

Proactive Risk Management

Audit & Compliance Confidence
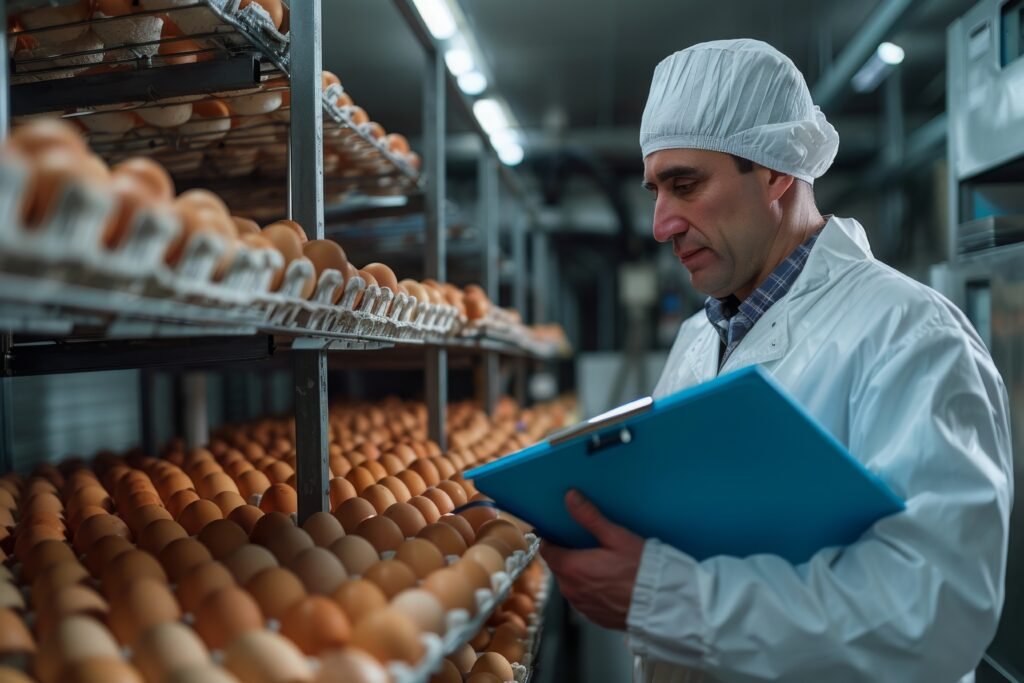

Designed for Manufacturing Environments
Syllabus Overview
1. Describe the procedures for contamination control and cross-contamination.
2. Identify the key phrases that are related to food safety including:
3. Defining food safety and hygiene, contamination, food poisoning, hazard, risk control, monitoring, taking corrective measures, verifying and validating the actionable outcomes, safe food, food safety management and pathogen.
4. Realize the advantages of the best food management and protect against costs due to poor hygiene practices.
5. States the benefits reaped by food businesses, consumers and food handlers of the highest standards of food hygiene.
6. Highlights the moral, statutory and economic consequences of poor hygiene practices to consumers, food industries and food handlers.
7. Describe the necessity of food safety measures:
8. Analyse the latest occurrences of reported food-borne illnesses related to causative organisms and food vehicles and find out the causes for seasonal changes in reported occurrences.
9. Illustrate the nature of various food types:
10. Determine the major characteristics of low-risk, high risk and ready-to-eat raw foods and their related risks.
11. Assess the microbial, physical, chemical and allergenic hazards
12. Provide examples of physical hazards, chemical hazards, and food safety hazards.
13. Explain the potential impacts if food safety hazards are not controlled.
2. Describes the shape, size and structure of bacteria and the major types of bacteria.
3. Realize the temperature range of the danger zone and optimum temperatures for the growth of bacteria.
4. Causes for bacterial growth, multiplication and factors that influence bacterial growth
5. Timescales involved in the multiplication of bacteria and the need for a bacterial growth curve.
6. Methods to destroy microbes
7. Heat, and chemical usage
8. Understand the principles of preservation methods.
9. Comprehend the formation of bacterial spores and toxins and their associated hazards in the food industry
10. Illustrate about ‘bacterial spores’ and find the role of spores in bacteria survival and understand the conditions in which spores form and their potential effects.
11. How toxins are produced are bacteria and differentiate exotoxins and endotoxins.
12. Find out the causes and signs of spoilage
13. Determine the control measures for microbial and enzyme control
2. Major differentiating factors between food-borne illnesses and food poisoning
3. Find out the differences between toxic and infectious reasons behind food-borne illnesses.
4. How to control the causes of food poisoning
5. Realize the people who are exposed to food poisoning.
6. Find out the causes, symptoms, incubation periods and control measures for principal pathogens, and food-related viruses
7. Know-how on the role of the supervisors, managers and food handlers in outbreaking the investigations.
2. Find out the role of management related to achieving the highest standards in personal hygiene and avoiding food contamination.
3. Determine the uniqueness of protective clothing for food handlers
4. Understand the key legal regulations for personal hygiene
5. Familiarity with the significance of excluding ill food handlers and accentuating the guidelines for fitness to work food handlers.
6. Equip the advantages and constraints of medical screening for food handlers.
2. The requirement for and advantages of staff training and maintaining training records
3. The need for planned training and its associated benefits for food businesses.
4. Legal guidelines for training food handlers
5. Consider aspects to develop and implement a food safety training programme.
6. Why consider the role of staff, their experience and skill and ways to overcome constraints such as language or literacy
7. Analyze the methods for effective communication related to food safety responsibilities.
8. Illustrate the information sources and guidance to develop a food safety training program.
2. Identify the hazards present in the organizational operation processes
3. Figure out the need for temperature control for specific businesses
4. Get to know the control actions and monitoring activities for food purchase, supplier segments, receipt and storage.
1. Describe the needs of site selection, finishes and construction materials
2. The role of management regards the construction of food premises, equipment and satisfactory design.
3. Significance of linear workflow
4. Right provision for washing requirements, lighting, ventilation and waste disposal
5. Legal regulations for designing and maintaining food premises
6. The role of management is related to principles and the need for cleaning and disinfection.
7. Part of management for organized systems, controlling and monitoring disinfection and cleaning for safe production of food
8. Statutory needs for cleaning and disinfection of food premises
9. Functionalities and nature of cleaning chemicals
10. Effective cleaning through schedules
11. Food pests and their habits
12. Principles of pest control
13. Points to remember while choosing a pest control contractor
2. HACCP concept and knowledge to execute an effective food management system
3. Ways to monitor and record food safety hazards
4. Action measures in scenarios where food safety hazards are uncontrollable
5. How to measure the effectiveness of food safety management procedures.
Ready to get skills for safe production and consumption practices? Enrol in the Highfield Level 4 Award in Food Safety Management for Manufacturing.
Benefits of this Course

Global Recognition
Custom Programs

Infinite Career Growth
Ongoing Support
Assessment & Certification
Validating Your Expertise to earn this certificate, you will complete:

Upcoming Batches
| Start Date | Duration | Time | Mode |
| – | – | – | – |
Regional Contact Numbers
Get in touch with our offices across different locations
Safety Courses
Trending Safety Courses

Diploma in Fire & Industrial Safety Management

IOSH Managing Safely

Diploma in Offshore Rig Oil and Gas Safety Engineering
Frequently Asked Questions
Is this course suitable for non-manufacturing sectors?
Is the certificate internationally recognised?
How long is the course?
Register Now

